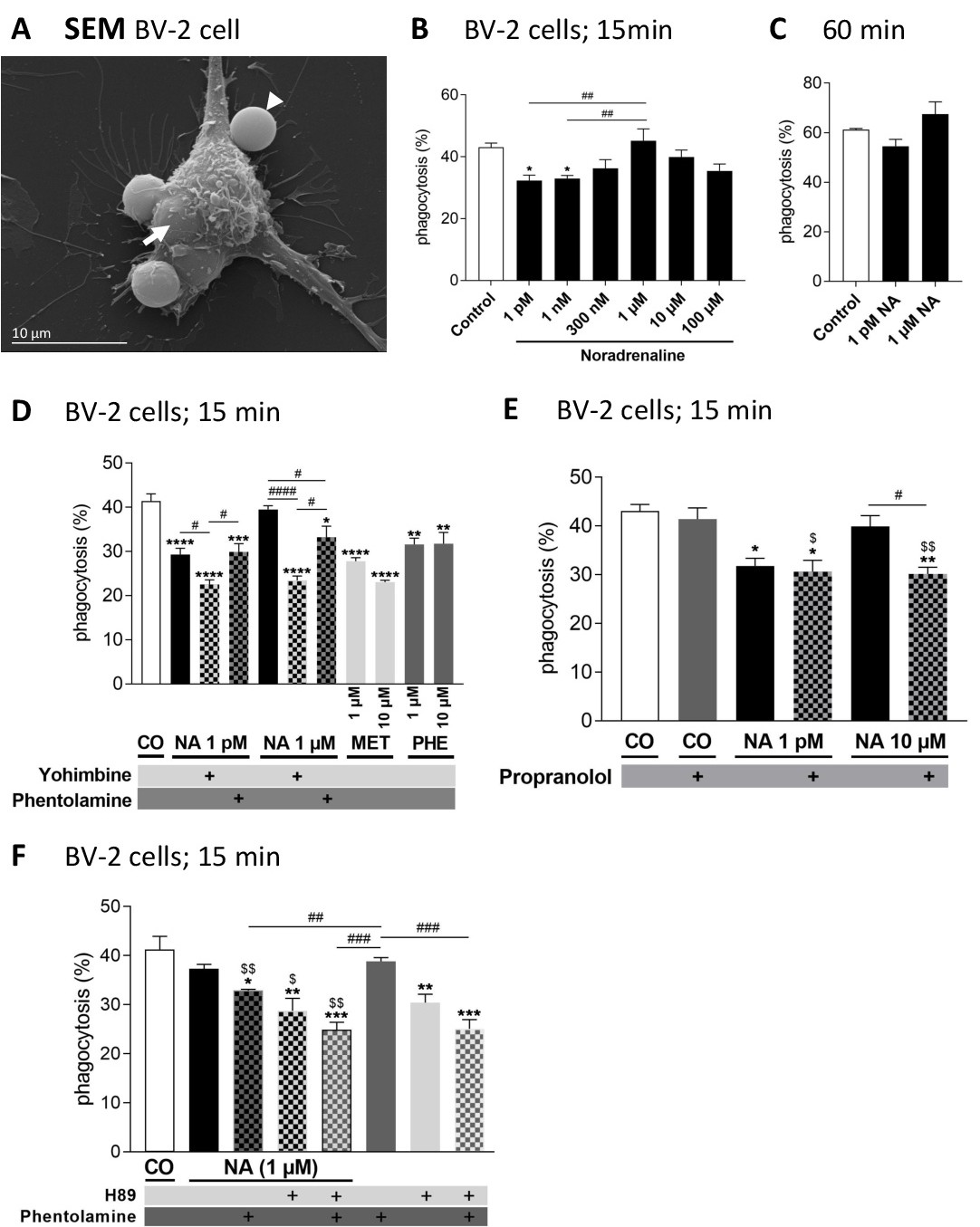
Fig. 7. Noradrenergic suppression of IgG-coated microspheres uptake is mediated by α- and β-adrenergic receptors. Scanning electron microscopic evaluation of microsphere-uptake by BV-2 cells showing that application of α- or β-adrenergic antagonists or agonists as well as suppression of PKA with H89 modulates microsphere uptake. In most experiments, cells were exposed to the drugs for 15 min. In the experiments shown in panel C, cells were exposed to NA for 60 min. Microsphere uptake is normalized to the total number of cells analyzed. Data are shown as means崆EM. (A) Representative BV-2 cell showing attached (one example is shown with an arrowhead) as well as engulfed (one example is shown with an arrow) microspheres. (B) Microsphere-uptake across different NA concentrations. One-way ANOVA revealed a significant suppressive effect between control and 1 pM or 1 nM NA. (C) Bath application of NA for 60 min did not reveal a significant difference between NA and control. (D) Co-application of NA and yohimbine (α2- adrenergic antagonist) or NA and phentolamine (α1- and α2-adrenergic antagonist) as well as application of metaraminol (α1- and α2-adrenergic agonist) and phenylephrine (α1-adrenergic agonist) in the absence (control, CO) and presence of adrenergic agonists (noradrenaline, NA; metaraminol, MET; phenylephrine, PHE) and/or antagonists (Yohimbine, Phentolamine). One-way ANOVA revealed significant differences between control and most treatment conditions (*). Pairwise comparison revealed significant differences between 1 pM NA and co-application of NA and yohimbine, 1 然 NA and co-application of NA and yohimbine, as well as 1 然 NA and co-application of NA and phentolamine (#). (E) Co-application of NA and propranolol (β-adrenergic antagonist). One-way ANOVA revealed significant differences if compared to control (*) or propranolol treatment (#). Pairwise t-test showed a significant difference between 10 然 NA and co-application of NA and propranolol. Comparison of NA (1 pM or 10 然) alone and NA in the presence of propranolol is indicated by $. (F) Co-application of H89 (PKA antagonist) and phentolamine. One-way ANOVA revealed significant differences when compared to control (*) or H89 treatment (#). Means崆EM; * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001, **** p<0.0001 denote significant difference when compared to control [white bar]; # p<0.05, ## p<0.01, ### p<0.001 denote significant difference when compared to phentolamine [PHE; dark grey bar]); $ p<0.05, $$ p<0.01, denote significant difference when compared to 1 然 NA alone.